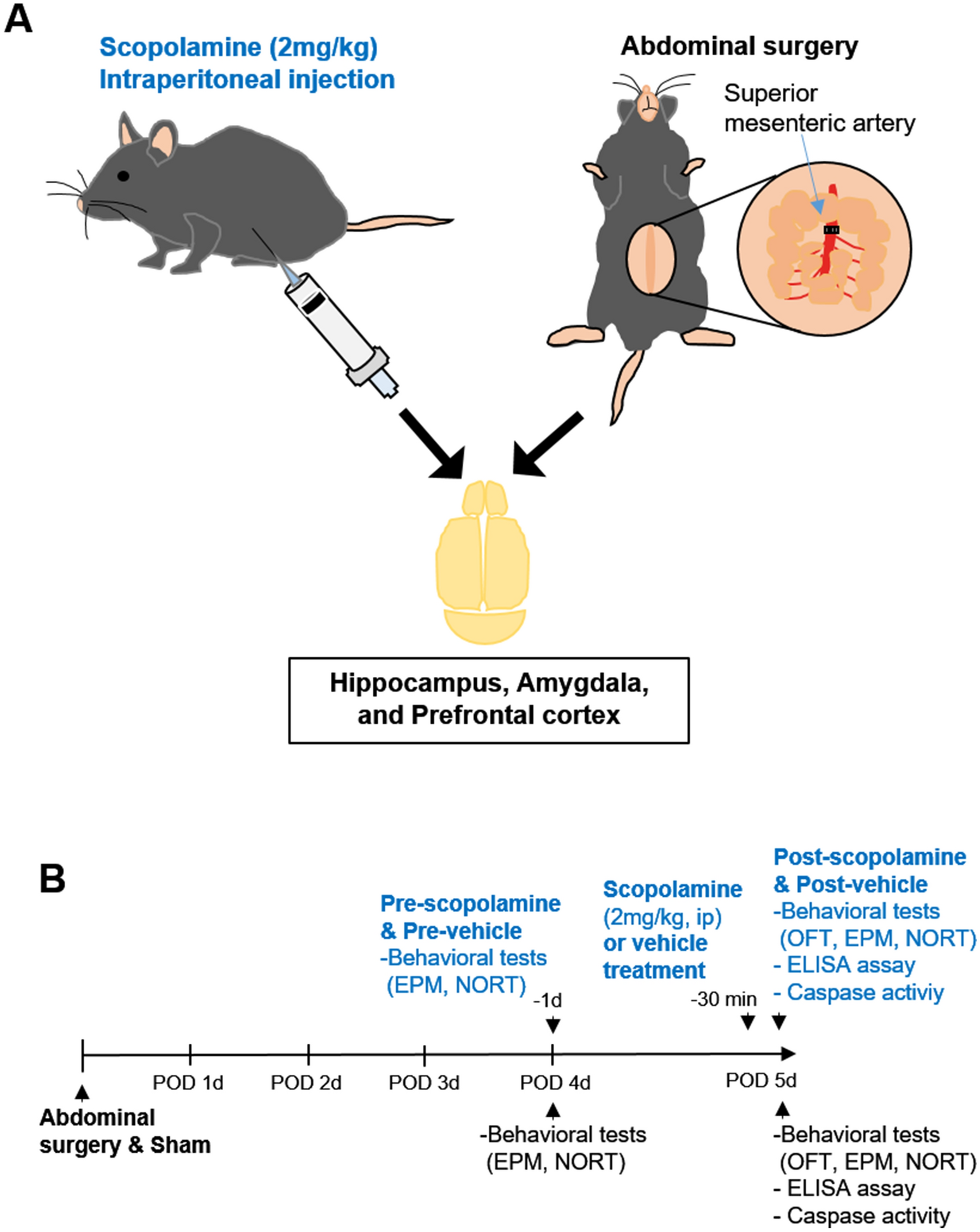
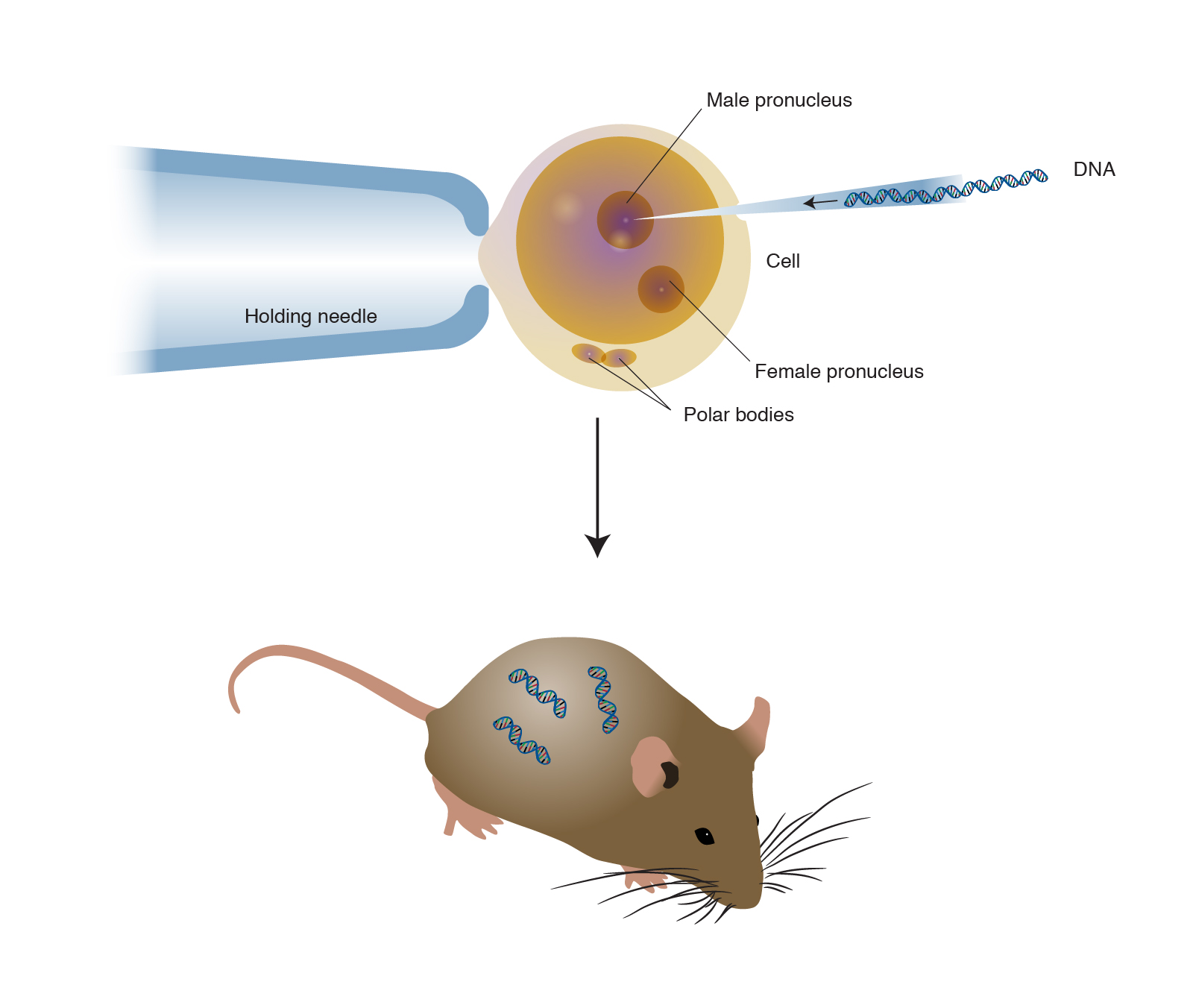
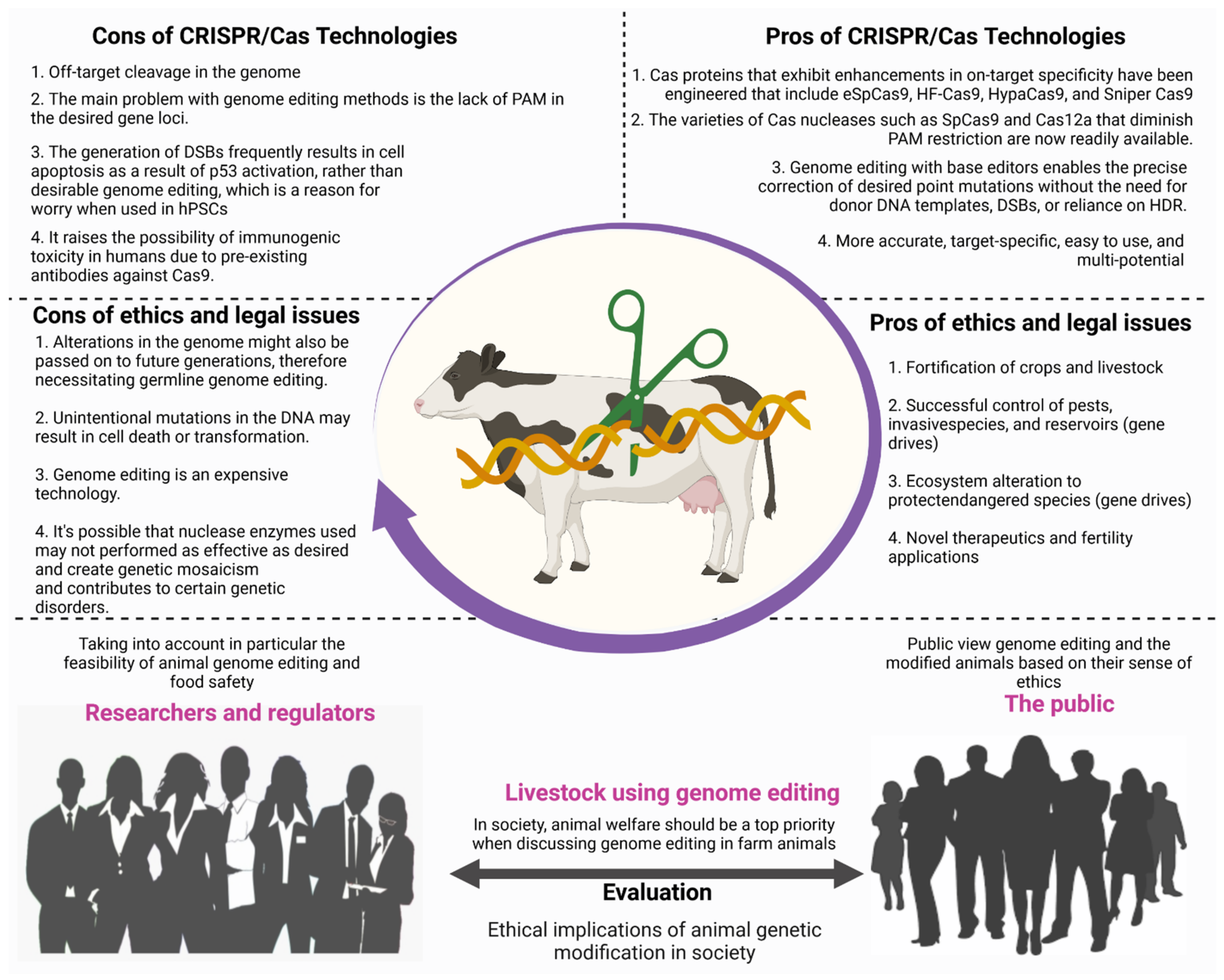
Transgenic Animals Applications Ppt
_1602913203_391831-4.jpg)
Transgenic farm animals are important in human medicine as a source of biologically active proteins as donors in xenotransplanta- tion and for a research in cell and gene therapy.
Transgenic animals applications ppt. 1 Assistant Professor 2 Associate Professor Department of Pharmacology Pravara I. The transgenic animals are genetically engineered and are also known as genetically modified organisms. PowerPoint PPT presentation.
Transgenic animals 1. Transgenic animals that produce useful biological products can be created by the introduction of the portion of DNA or genes which codes for a particular product such as human protein a-1-antitrypsin used to treat emphysema tissue plasmogen activator goat blood clotting factors VIII and IX sheep and lactoferrin cow. Industry and medicine have taken advantage of these animals a lot.
One of them is the ability to engineer transgenic animals. The development of transgenic animals has been part of biotechnology research which has been expanding rapidly. A transgenic animal has been genetically engineered to incorporate a foreign gene.
Transgenic animals can be used as disease models transpharmers xenotransplanters food sources and other biological models. Transgenic animals and their application in medicine Bagle TR 1 Kunkulol RR 2 Baig MS 3 More SY 4. Transgenesis is the process by which mixing up of genes takes place.
Applications Transgenic models for Alzheimer disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Huntington disease arthritis muscular dystrophy tumorigenesis hypertension neurodegenerative disorders endocrinological dysfunction coronary disease etc. Transgenic animals produced with. Cohen and Herbert Boyer.
Typical agricultural application include improved carcass composition lactation. Methodology Retrovirus vector DNA microinjection Engineered embryonic stem cell Cre. Transgenic animals are used as tools in research and for the production of recombinant proteins The main applications of transgenic animals are described as followsStudying gene function.

_1602913203_391831-15.jpg)
_1602913203_391831-3.jpg)
_1602913203_391831-12.jpg)

_1602913203_391831-5.jpg)
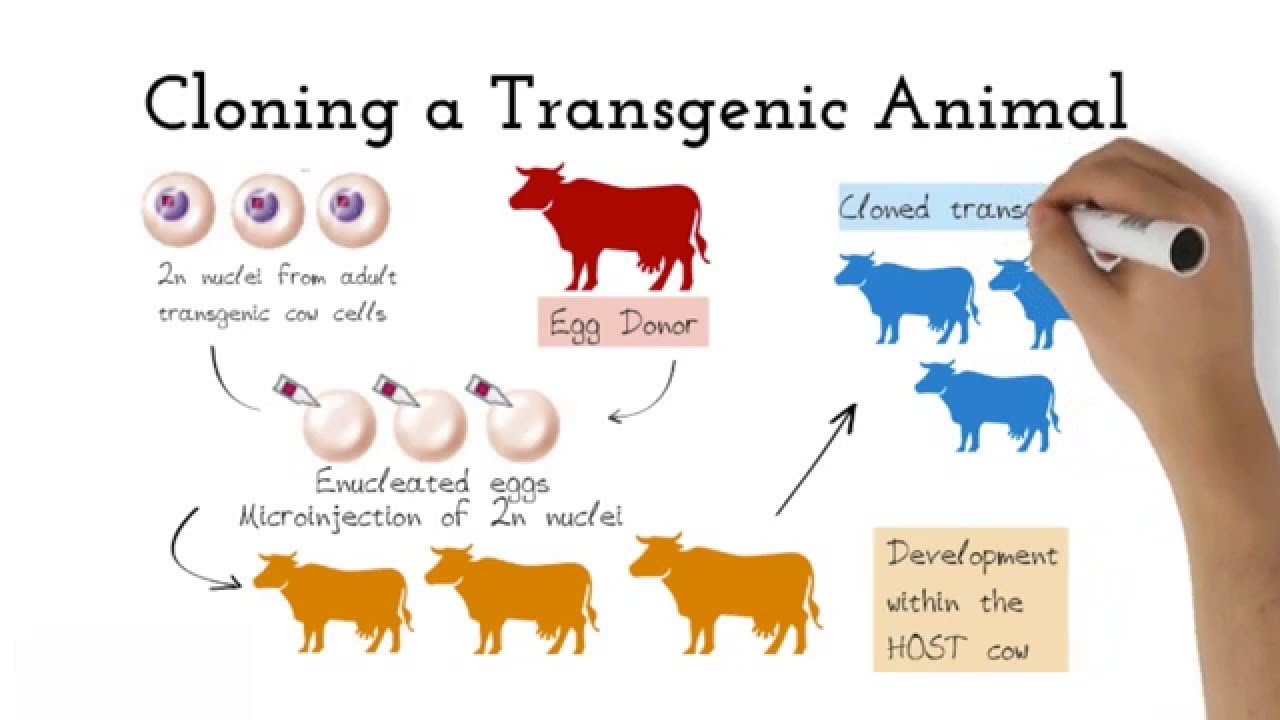

_1602913203_391831-2.jpg)