Cellular Respiration Meaning In Biology

Autotrophs like plants produce glucose during photosynthesis.
Cellular respiration meaning in biology. Cellular respiration Cellular respiration n. The respiration occurring at the cellular level wherein the cells produce energy by combining oxygen with food molecules is called cellular respiration. The process plays an essential role in maintaining the biological functions of all living cells.
Aerobic respiration requires oxygen to fully oxidise the organic molecule. In the cells of any non-photosynthetic eukaryote such as a person bread mold or a paramecium glucose and oxygen are going to come from outside the cell. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter.
A series of metabolic processes that take place within a cell in which the biochemical energy is harvested from an organic substance eg. Cellular respiration biology definition. Cellular respiration stores chemical energy in the form of phosphorylated nucleotides primarily ATP by means of oxidative reactions and makes it available to other reactions.
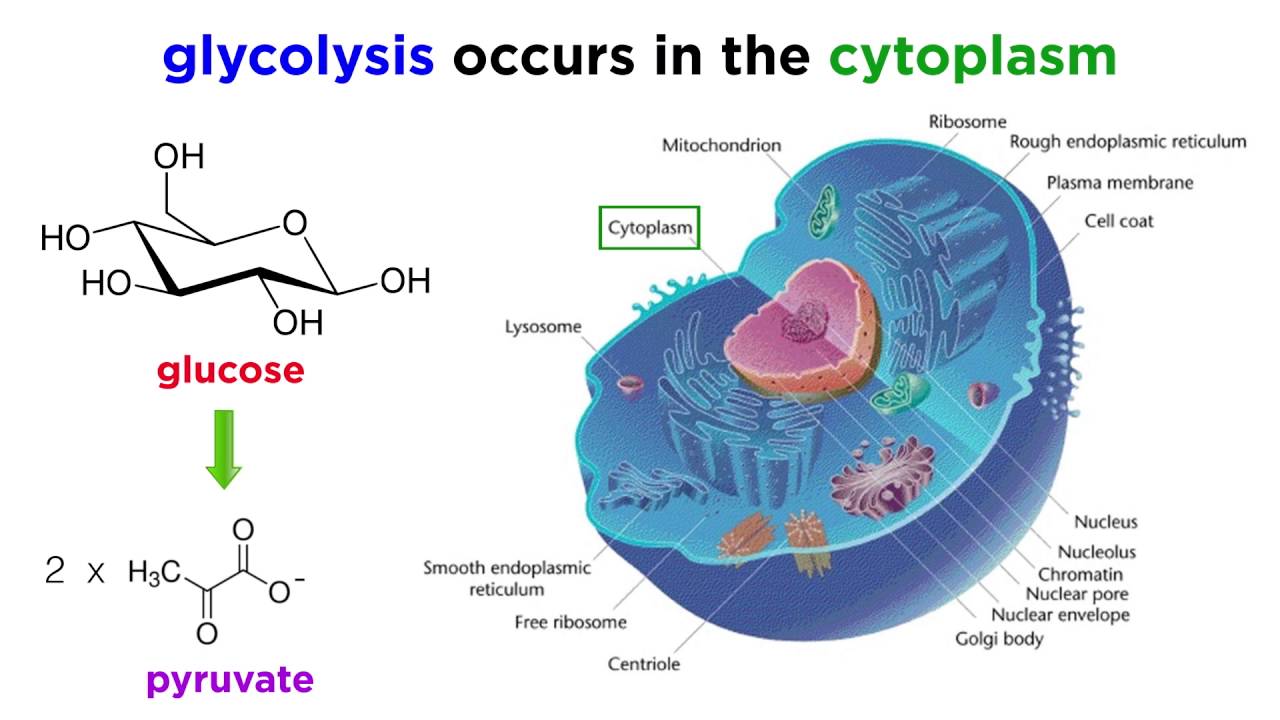
The principal carbohydrate formed through photosynthesis is glucose. Cellular respiration is a biological process in which cells convert sugar amino acids and fatty acids into energy utilized by the cell. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis pyruvate oxidation the citric acid or Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.
The process of cell catabolism in which cells turn food into usable energy in the form of ATP. To create ATP and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy into a useable form. Other types of organisms such as animals fungi many protozoa and a large.
But cellular respiration is slightly more complicated than just converting the energy from glucose into ATP. Cellular respiration is a process that all living things use to convert glucose into energy. The cellular context In the diagram at left 1 represents the cell exterior.